Real Examples Of Government Setting Price Floors For Agriculture

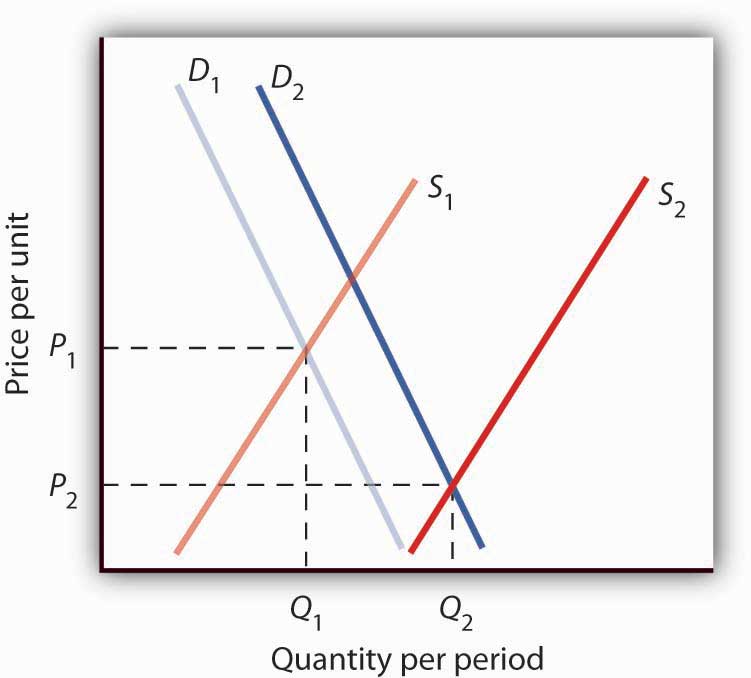
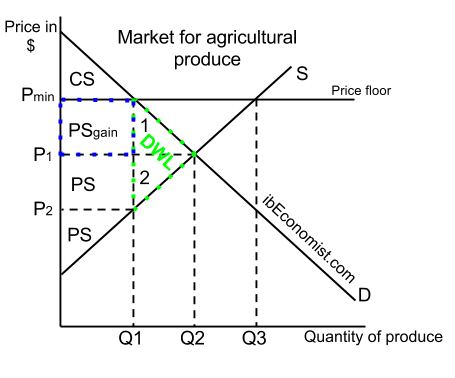
However a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling.
Real examples of government setting price floors for agriculture. Real world price ceiling example. If minimum prices are set above the equilibrium it will cause an increase in prices. A price floor is a minimum price enforced in a market by a government or self imposed by a group. A minimum allowable price set above the equilibrium price is a price floor with a price floor the government forbids a price below the minimum.
Similarly a typical supply curve is. Governments often seek to assist farmers by setting price floors in agricultural markets. Other price floors include regulated us airfares prior to 1978 and minimum price per drink laws for alcohol. That s because a price ceiling is a maximum rather than an exact required price.
A minimum allowable price set above the equilibrium price is a price floor a minimum allowable price set above the equilibrium price with a price floor the government forbids a price below the minimum. A price floor example the intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e0. Farmers would thus receive the market price of 3 plus a government payment of 1 per unit. Governments often seek to assist farmers by setting price floors in agricultural markets.
It tends to create a market surplus because the quantity supplied at the price floor is higher than the quantity demanded. If the government purchases the surplus crop it is at taxpayer expense. A look at some examples of current price floors and ceilings in today x27 s economy shows that there are complex consequences. Governments or other organizations may use price floors or ceilings to impose a price that is suitable for certain groups of consumers or producers.
Two common price floors are minimum wage laws and supply management in canadian agriculture. It is argued farmers incomes are too low. Governments use price floors to keep certain prices from going too low. For example the eu has used minimum prices for agriculture.
Agriculture experiences similar market distortions when the government institutes price floors for crops. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied qs exceeds the quantity demanded qd. Demand curve is generally downward sloping which means that the quantity demanded increase when the price decreases and vice versa. A minimum price is when the government don t allow prices to go below a certain level.
For instance if the government sets the ceiling for potatoes at 5 per pound but the equilibrium price for potatoes is already 4 per pound this would have no real effect on the price of potatoes.